- Hotline +65 6631 8332
Diving into Payment Gateway Working Model - Making the Complex Simple
Tuesday, 06 Feb, 2024

This article is a part of PayCEC payment insights
Follow PayCEC - global payment gateway to get updates on the latest payment trends and ecommerce news
What's inside?
The projected worldwide e-commerce sales are astonishing, rising from an expected USD 2.8 trillion by the end of 2018 to a stunning USD 6.3 trillion by 2023.
With digital shopping quickly developing globally, it is critical for e-commerce enterprises, whether new or established, to provide easy and secure payment ways to their consumers.
Payment gateways emerge as the preferred method, allowing for the quick and easy transmission of transaction data from a payment portal to the acquiring bank.
Before delving into the payment gateway working model, we must understand what a payment gateway is.
Inside a Payment Service Provider Business Model

Discover the payment gateway model that turns every click into a smooth shopping experience.
1. Payment Gateway:
Central to the payment gateway business model is the payment gateway itself, a specialized service that facilitates the secure transfer of payment data between e-commerce platforms and financial institutions.
The choice of a payment gateway is a strategic decision for merchants. Different payment gateways may offer varying features, pricing structures, and levels of security.
Business owners often select a payment gateway based on their specific business needs, customer preferences, and the geographic locations they serve.
2. Merchant Account:
A merchant account is a dedicated account established by a business to receive funds from completed transactions.
In the payment gateway working model, it is the destination for the settled funds, ensuring sellers receive the payments from successful transactions. A merchant account is typically a prerequisite for integrating a payment gateway.
Merchants may work with financial institutions or payment service providers to set up and manage their merchant accounts. Moreover, the choice of provider can impact the overall efficiency of the payment process.
3. Customer's Financial Institution:
The customer's financial institution, potentially a bank or a credit card issuer, plays a central role in the payment gateway model.
It is responsible for verifying the authenticity of the payment details, checking for available funds, and authorizing or declining the transaction based on the customer's financial standing.
What makes this relationship dynamic is the real-time communication between the payment gateway and the customer's financial institution.
It's a high-stakes conversation where the financial institution's response to the authorization request becomes the make-or-break moment for the transaction.
4. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Encryption:
SSL encryption is a fundamental security measure employed in the payment gateway working model.
It ensures the secure transmission of sensitive customer information, such as credit card details, between the customer's browser and the e-commerce platform. This encryption safeguards the data from potential interception or unauthorized access.
The technology uses advanced cryptographic algorithms to encrypt the data, rendering it unreadable to anyone attempting to intercept the information.
SSL encryption is frequently displayed by a padlock icon in the browser's address bar, giving clients the comfort that their data is delivered safely.
5. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) Compliance:
PCI DSS is a set of security standards designed to ensure the secure handling of payment card information.
Compliance with PCI DSS is a non-negotiable aspect. It involves implementing specific security measures, conducting regular security assessments, and maintaining a secure network infrastructure.
PCI DSS payment gateways and merchants adhere to these standards, protecting the confidentiality and integrity of customer payment data.
6. Fraud Prevention Mechanisms:
Fraud prevention is integral to the payment service provider business model, providing an additional layer of security against unauthorized transactions.
These mechanisms may include real-time fraud detection algorithms, address verification systems (AVS), and 3D Secure protocols. The goal is to identify and prevent fraudulent activities before they can impact the completion of a transaction.
The dynamic nature of online transactions necessitates proactive measures to combat fraud. Payment gateways employ sophisticated algorithms and tools to analyze transaction patterns, detect anomalies, and trigger alerts for further investigation.
How a Payment Gateway Business Model Works

Behind the scenes of the payment gateway model that powers stress-free transactions.
1. Initiating the Transaction:
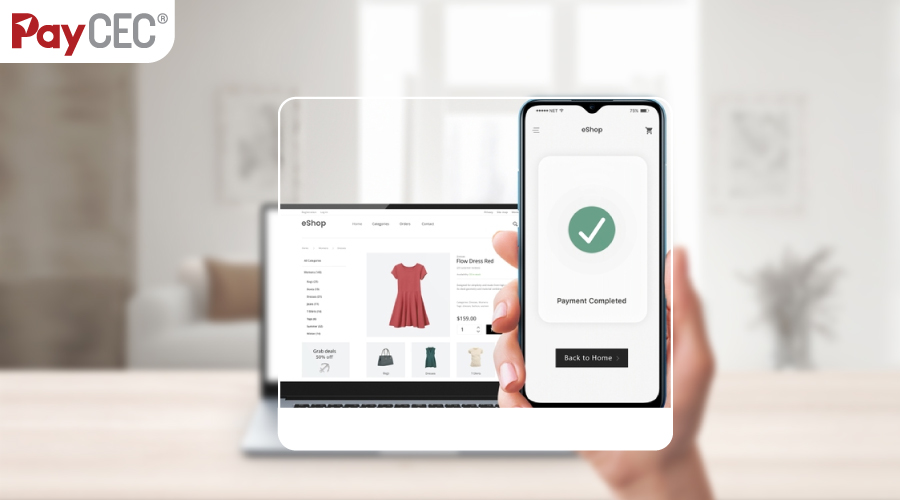
The journey of a financial transaction begins when a customer initiates a purchase on an e-commerce platform.
The initiation phase involves the customer providing details such as the selected items, billing information, and preferred payment method.
This information is the foundation for the subsequent stages of the payment gateway working model, guiding the transaction through a series of secure and standardized steps.
Encryption and Security Protocols:
One of the paramount features of the payment gateway model is the implementation of encryption and security protocols.
Encryption is achieved through secure sockets layer (SSL) technology. This advanced cryptographic protocol secures the information between the customer's browser and our e-commerce platform, protecting it from any potential interception or unauthorized access.
The integration of stringent security measures is fundamental to maintaining the integrity of the payment process, ensuring a secure and reliable experience for everyone involved.
2. Transmission to the Payment Gateway:
Following the input of the customer's payment details, the data undergoes secure transmission to the payment gateway.
The payment gateway serves as a middleman between the e-commerce platform and the financial institutions in charge of transaction processing.
It serves as a conduit, transmitting encrypted payment data to the subsequent stage of the transaction flow.
3. Authorization Request:
This step involves verifying the authenticity of the payment details, checking for available funds or credit, and ensuring that the transaction aligns with the customer's financial profile.
The authorization request is a critical juncture in the payment gateway business model. It involves real-time communication between the payment gateway and the customer's bank or credit card issuer.
The financial institution responds to the request, either approving or declining the transaction, based on factors like available funds, credit limit, and potential fraud alerts.
4. Transaction Approval or Decline:
The determination of the transaction outcome is contingent upon the response from the customer's financial institution.
In the event of an accepted authorization request, the payment gateway directs the e-commerce platform to proceed with completing the transaction. Conversely, if the request is declined, the payment gateway promptly notifies the consumer and the e-commerce platform.
The swift and accurate communication between the payment gateway and the financial institution is essential. In the case of approval, the transaction progresses seamlessly, and the customer receives confirmation of a successful purchase.
In the event of a decline, the payment gateway model provides transparency to the customer regarding the reason for the denial, enabling them to take appropriate action.
5. Transaction Settlement:
Upon receiving approval, the payment gateway facilitates the settlement of the transaction. Settlement involves the transfer of funds from the customer's financial institution to the merchant's account.
This process typically occurs within a predetermined time frame, ensuring merchants receive the funds from successful transactions promptly. Timely and correct settlement is critical for preserving a company's financial health and guaranteeing a smooth cash flow.
6. Transaction Confirmation:
The final stage of the payment gateway business model involves providing the customer and the e-commerce platform with a confirmation of the completed transaction.
This confirmation functions as a receipt, providing details about the purchase, including the items acquired, the total amount paid, and relevant transaction information.
Moreover, it is a valuable reference for merchants, aiding in meticulous record-keeping and facilitating efficient order fulfillment operations. The confirmation signifies the smooth execution of the payment gateway model.
And that is a brief review of the payment gateway working model. Let’s dive deeper into how a payment gateway works, allowing you to make a better decision on what to choose.
How Does a Payment Gateway Make Money?

Now we have covered the technical basics, let's examine the payment gateway revenue model.
Understanding the sources of income for payment gateways unveils a complex yet essential aspect of the digital transaction landscape.
Transaction Discounting Rate (TDR):
At the heart of a payment gateway revenue model lies the Transaction Discounting Rate (TDR), the transaction processing fee levied on each successful transaction coursing through the gateway's infrastructure.
Expressed as a percentage of the transaction value, the TDR varies depending on the chosen payment method.
Some gateways adopt a hybrid model, charging a fixed monthly fee in addition to the TDR, benefiting businesses engaged in high transaction volumes. Alternatively, some gateways forgo fixed rates, relying solely on a higher TDR.
Charges on International Transactions:
As the digital marketplace transcends borders, payment gateways often charge a premium TDR for transactions involving multiple currencies.
This approach acknowledges the additional complexities and risks associated with cross-border financial exchanges, providing gateways with compensation for facilitating international transactions.
Maintenance and Support Costs:
Businesses leveraging payment gateways are not exempt from additional costs. Annual maintenance charges, coupled with fees for technical support, constitute a payment gateway revenue model.
These costs ensure ongoing service reliability, security updates, and responsive assistance, contributing to the seamless functioning of the payment ecosystem.
Setup Fees:
Initiating a partnership with a payment gateway comes with a setup fee. This one-time cost varies across gateways and covers the administrative expenses associated with onboarding a new business onto their platform.
Overcoming Payment Gateway Challenges: How PayCEC Leads the Way

PayCEC turns challenges into opportunities for secure digital commerce.
While the payment service provider business model is pivotal in facilitating online transactions, businesses often grapple with various hurdles that range from security concerns to stress-free integrations.
Let's dive into these challenges and discover how PayCEC confronts them head-on and turns them into opportunities for secure digital transactions.
Fraud-Busting Vigilance:
The online world is a playground for fraudsters, and detecting and preventing fraudulent activities is a constant challenge.
PayCEC tackles this with a superhero-level fraud prevention mechanism. Picture it as an ever-watchful guardian, using advanced algorithms to thwart fraudulent activities, safeguarding businesses and consumers.
Global Transaction Smoothness:
With businesses spreading their wings globally, the payment gateway working model must speak the language of multiple currencies and diverse payment methods.
Enter PayCEC, a global virtuoso that facilitates transactions in multiple currencies and payment methods. It's like a digital passport for businesses, enabling international expansion without the usual headaches.
Technical Compatibility Wizardry:
Integrating payment gateways with various e-commerce platforms can feel like untangling a web. Technical glitches often disrupt the payment process. PayCEC comes to the rescue with compatibility wizardry that ensures smooth integrations.
It is the payment gateway business model that effortlessly blends with various e-commerce platforms, minimizing disruptions and ensuring a user-friendly payment experience.
Key Takeaways
A payment gateway working model provides a pillar of security, efficiency, global expansion, and trust-building. Embracing it allows online businesses to thrive and sets them on a trajectory for sustained success.
While challenges in the payment gateway realm are real, PayCEC transforms them into stepping stones for a brighter digital future.
It is a guardian, a global companion, and a tech whisperer – all rolled into one. With PayCEC, the online transaction journey is a delightful and secure experience for all.
About PayCEC
PayCEC was established in response to the growing need of businesses to accept online payments more quickly and easily. In the new media era, our payment flow has evolved to work seamlessly and effectively across all platforms and devices. We pride ourselves on combining superior technology with first-class customer service.
PayCEC is a truly global payments platform that not only allows customers to get paid but also withdraws funds to their business accounts in various currencies.
We have created an open and secure payments ecosystem that people and businesses choose to securely transact with each other online and on mobile devices.
PayCEC Team
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the PSP business model?
-
What's a PSP and What Do They Do?
Think of a PSP as the middleman in the digital money game. They ensure that when you buy something online or use a mobile payment app, the money gets from your account to the seller's account without hiccups.
-
How PSPs Make Money
PSPs make their cash by taking a small cut from each transaction. It is a tiny fee every time money changes hands through their platform. They also charge businesses a subscription fee for using their services regularly. These fees add up and keep the PSPs in business.
-
Going Global: Why It Matters
PSPs aren't just about local transactions. They learn to work with different rules and cultures in various parts of the world. Like a band going on a world tour, they want to make their financial symphony heard everywhere.
-
Staying Cool with Tech Trends
PSPs keep up with the latest tech trends like blockchain, artificial intelligence, and contactless payments.
It isn't just about staying cool but meeting the demands of a tech-savvy audience and keeping transactions secure and efficient.
As we move further into the digital economy, knowing about the PSP business model puts us at the forefront of a future where online payments happen seamlessly around the globe.
So, the next time you make an online purchase or pay with your phone, remember there's a PSP behind the scenes that keeps the digital symphony of payments playing.
Is payment gateway a Fintech?
To discover if payment gateways are part of FinTech, we should understand that FinTech is about using technology for all things money. Payment gateways fit right into this because they use technology to make online money exchanges secure and easy.
In the big show of FinTech, payment gateways act like conductors. They organize and ensure money moves smoothly, validate payments, and keep everything safe online.
Payment gateways earn money by taking a small fee for each transaction and a small piece of the total amount. It helps them keep the digital money world running smoothly and contributes to how FinTech works on a bigger scale.
In the face of escalating cyber threats, payment gateways prioritize advanced encryption technologies and tokenization to fortify transactions against the dynamic landscape of cyber risks, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of financial data.
Beyond their transactional role, payment gateways also help make sure everyone, big or small, can be part of the digital money world. They connect traditional and digital finance, making it easier for businesses of all sizes to join.
How much do payment gateways make?
Think like this: every time you make an online purchase, a small fee, typically ranging from 1.5% to 3% of the transaction value, is taken by the payment gateway.
However, the payment gateway revenue model doesn't conclude there. Payment gateways often earn a percentage of the transaction, from $0.20 to $0.50.
This dual-layered approach ensures that as the volume and value of digital transactions rise, so does the revenue stream for these financial facilitators.
In addition to fixed fees, payment gateways often capture a percentage of the transaction value. This dynamic fee structure aligns their interests with the growth of digital transactions.
As the volume of financial activity expands, so does the harmonic crescendo of income, indicating a symbiotic relationship between firm financial health and payment gateway profitability.
When transactions traverse international waters, payment gateways often charge additional fees. These fees account for the complexity of navigating diverse regulatory frameworks and contribute to the payment gateway revenue model.
Moreover, subscription models are a notable revenue stream for payment gateways. Businesses seeking continuous access to the services and security offered by these digital conductors opt for subscription plans.
These recurring payments further solidify the revenue foundations of payment gateways, providing stability amidst the dynamic currents of digital transactions.
News
Business
Products

who we are
about us
We are honored to serve as your reliable business partner and financial service provider in the industry and other business-related services. With the help of our professional staff, to help merchants to achieve their goals for the development and expansion of the international business market.
Our payment flow has developed in the e-commerce world to perform seamlessly and effectively across all platforms and devices. We take pleasure in combining technology with customer service, to solve your concerns at the moment.
PayCEC is a fully worldwide payment network that not only allows merchants to be paid immediately and securely, but also allows them to withdraw money in multiple currencies to their company accounts.































 +65 6631 8332
+65 6631 8332






 Processing
Processing